UNIT 1: Supply & Demand
January 12th, 2016
Demand- the quantities that people are willing and able to buy at various prices.
Law of Demand- there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
 |
These are what causes a change in demand: |
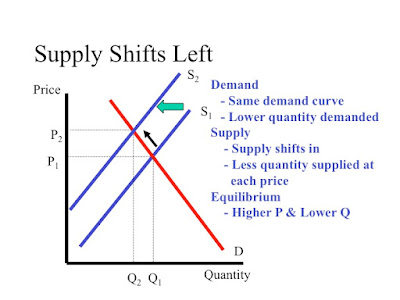
This is what a shift in supply looks like.
Supply: quantities producers/ sellers are willing & able to produce in various prices.
Law of Supply: states that there is a direct relationship between price and quantity supply.